Ribeye Steak vs. Other Cuts of Beef: Ribeye Steak Nutrition Facts
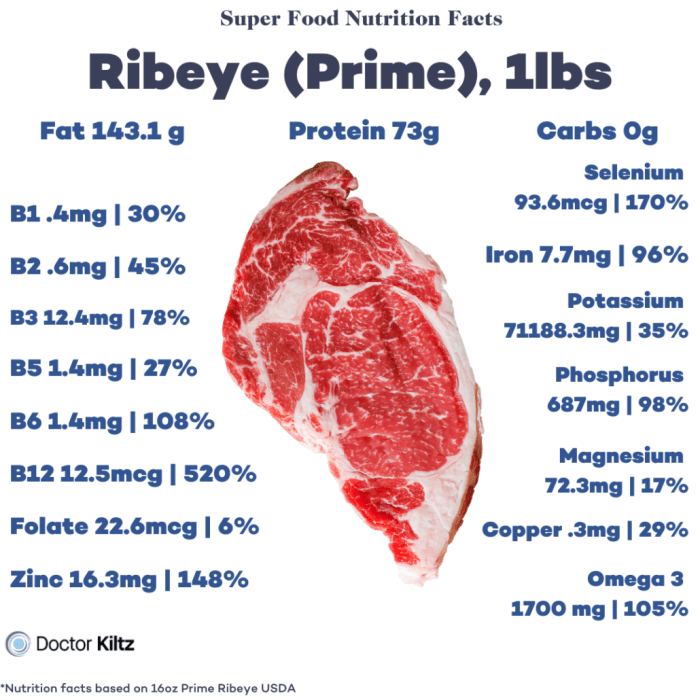
Ribeye steak nutrition facts – Ribeye steak, renowned for its rich marbling and intense flavor, occupies a distinct position within the spectrum of beef cuts. Understanding its nutritional profile relative to other popular choices is crucial for making informed dietary decisions. This section will compare and contrast ribeye with sirloin, tenderloin, and flank steak, highlighting key differences in fat content, marbling, and overall nutritional value.
Nutritional Comparison of Ribeye and Other Beef Cuts
The following comparison illustrates the nutritional variations among ribeye, sirloin, tenderloin, and flank steak. These values are approximate and can vary based on factors like the animal’s diet and the specific cut. It’s always best to check the nutrition label on the specific package purchased.
- Ribeye: Higher in total fat and calories, significantly higher in saturated fat, but also richer in certain vitamins and minerals due to the marbling. Offers a more intense flavor profile.
- Sirloin: Leaner than ribeye, lower in total fat and calories, and a good source of protein. The flavor is less intense than ribeye.
- Tenderloin (Filet Mignon): Extremely lean, lowest in fat and calories among these cuts. Tender and mild in flavor, but can be less flavorful than ribeye.
- Flank Steak: Leaner than ribeye, but tougher and requiring longer cooking times. Offers a more robust, beefy flavor, though less intense than ribeye.
Fat Content and Marbling Differences
The significant difference between ribeye and leaner cuts lies in the fat content and marbling. Ribeye is characterized by abundant intramuscular fat (marbling), which contributes to its juicy texture and rich flavor. This marbling, however, significantly increases the total fat and calorie content. In contrast, sirloin, tenderloin, and flank steak have considerably less marbling, resulting in lower fat and calorie counts.
The visual difference is striking: a ribeye steak will display visible white streaks of fat throughout the muscle, while leaner cuts will appear predominantly red with minimal visible fat.
Nutritional Advantages and Disadvantages of Choosing Ribeye Steak, Ribeye steak nutrition facts
Choosing ribeye offers the advantage of a superior taste and texture experience due to its higher fat content and marbling. The marbling also contributes to a more tender and juicy final product. However, the higher fat content is a significant disadvantage for individuals watching their fat and calorie intake. Leaner cuts like sirloin or tenderloin offer a lower calorie and fat alternative while still providing a good source of protein.
Understanding ribeye steak nutrition facts is crucial for mindful eating. A comparison with other popular fast-food options, such as checking the in n out nutrition facts , can provide context for making informed choices. Returning to ribeye, remember to consider the cooking method and portion size when assessing its overall nutritional impact.
The choice ultimately depends on individual dietary preferences and health goals. A balanced diet incorporating various protein sources is generally recommended.
Health Implications of Ribeye Steak Consumption

Ribeye steak, renowned for its rich marbling and flavor, presents a complex nutritional profile with both potential benefits and drawbacks for health. Understanding these aspects is crucial for informed dietary choices. This section will explore the positive and negative health implications associated with ribeye consumption, considering factors such as portion size and frequency.
Protein and Micronutrient Benefits of Ribeye Steak
Ribeye steak is an excellent source of high-quality protein, essential for building and repairing tissues, supporting immune function, and maintaining overall bodily processes. A 3-ounce serving provides approximately 20-25 grams of protein, contributing significantly to daily protein requirements. Furthermore, ribeye contains various micronutrients, including iron, zinc, and B vitamins. Iron is vital for oxygen transport in the blood, while zinc plays a crucial role in immune function and wound healing.
B vitamins are essential for energy metabolism and nerve function. The specific micronutrient content can vary slightly depending on factors like the animal’s diet and breed. However, ribeye consistently provides a notable contribution to these essential nutrients.
Health Risks Associated with Ribeye Steak Consumption
The primary health concern associated with regular ribeye steak consumption is its high saturated fat and cholesterol content. Saturated fat contributes to elevated LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke. High cholesterol levels can also contribute to the development of atherosclerosis, a condition where plaque builds up in the arteries, restricting blood flow.
The high fat content of ribeye also contributes to a higher caloric density, potentially leading to weight gain if consumed in excess. It’s important to note that the risk level is directly related to the frequency and quantity of consumption.
Potential Positive and Negative Health Impacts of Ribeye Steak
| Factor | Positive Impacts | Negative Impacts |
|---|---|---|
| Protein Intake | Supports muscle growth and repair, boosts immune function, contributes to satiety. | High protein intake may be detrimental for individuals with kidney disease. |
| Micronutrients | Provides iron, zinc, and B vitamins, crucial for various bodily functions. | Micronutrient content may be overshadowed by negative impacts of high fat and cholesterol. |
| Saturated Fat & Cholesterol | None directly attributable to saturated fat and cholesterol. | Contributes to elevated LDL cholesterol, increasing risk of heart disease and stroke. Can contribute to weight gain if consumed in excess. |
| Portion Size & Frequency | Moderate consumption can provide valuable nutrients without excessive fat and cholesterol intake. | Large portions and frequent consumption significantly increase the risk of negative health impacts. |
Question & Answer Hub
Is ribeye steak suitable for weight loss diets?
While high in calories and fat, ribeye steak can be included in weight loss diets in moderation. Focus on portion control and balance it with plenty of vegetables and lean protein sources.
Can pregnant women eat ribeye steak?
Pregnant women can enjoy ribeye steak, but it’s crucial to ensure it’s cooked thoroughly to eliminate any risk of foodborne illness. Moderation is advised due to the fat content.
What are the best side dishes to pair with ribeye steak for a balanced meal?
To balance the richness of ribeye, pair it with nutrient-rich sides like roasted vegetables (broccoli, asparagus), a large salad, or quinoa.
Are there any specific cooking methods that minimize fat content when preparing ribeye steak?
Trimming excess visible fat before cooking and opting for grilling or broiling (allowing excess fat to drip away) can help reduce the overall fat content.
