Seaweed Salad in Different Diets

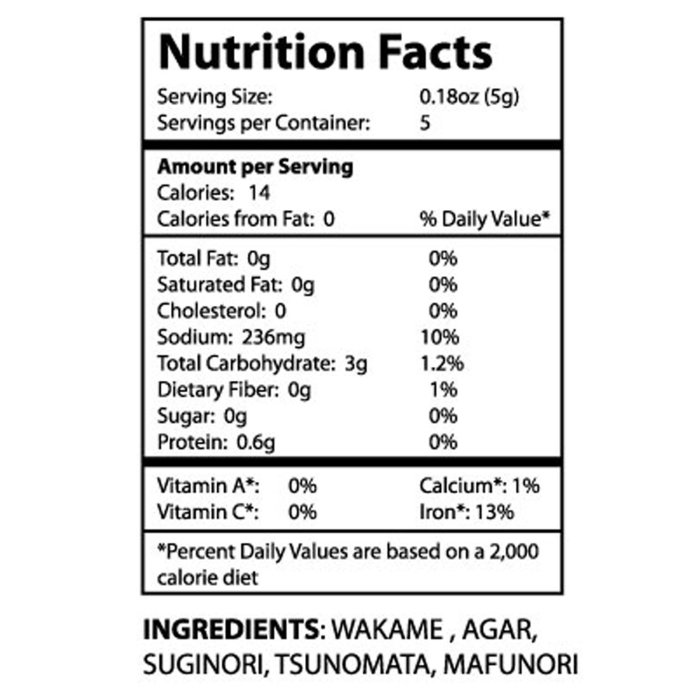
Seaweed salad nutrition facts – Seaweed salad’s nutritional profile makes it a versatile addition to various dietary plans, though its suitability depends on specific dietary needs and restrictions. Understanding its composition and potential interactions with different approaches is crucial for informed dietary choices.Seaweed salad offers a range of nutritional benefits, including vitamins, minerals, and fiber, making it a potentially valuable component of many diets.
However, certain considerations, such as sodium content and potential iodine levels, must be taken into account when integrating it into specific eating plans.
Seaweed Salad’s Suitability Across Different Diets
Seaweed salad is naturally vegan and vegetarian-friendly, as it contains no animal products. However, its suitability for ketogenic and low-sodium diets requires careful consideration. While low in carbohydrates, the sodium content can be high in some commercially prepared seaweed salads, making it less suitable for those on strict low-sodium diets. For ketogenic diets, the net carbohydrate content needs to be assessed on a per-serving basis, as it can vary depending on the type of seaweed and added ingredients.
Seaweed salad offers a surprisingly diverse nutritional profile, rich in vitamins and minerals. For a contrasting snack comparison, you might consider checking out the nutritional information for a different kind of snack, such as flat prezel nutrition facts , to see how they stack up. Returning to seaweed salad, its low-calorie nature and high iodine content make it a healthy addition to any diet.
Choosing low-sodium varieties and controlling portion sizes is key for both these diets.
Incorporating Seaweed Salad into Meal Plans
Seaweed salad’s versatility allows for easy integration into various meal plans.
- Vegan Meal Plan: Pair seaweed salad with tofu, edamame, and brown rice for a complete and nutritious meal. Alternatively, incorporate it into a Buddha bowl with various vegetables and a tahini dressing.
- Vegetarian Meal Plan: Serve seaweed salad alongside grilled halloumi cheese and a quinoa salad for a balanced and flavorful meal. It can also be a refreshing side dish to black bean burgers or lentil soup.
- Ketogenic Meal Plan: Use seaweed salad as a low-carb side dish with grilled salmon or chicken. Be mindful of added ingredients like sesame oil or soy sauce which may increase carbohydrate content. Ensure you check the nutrition label for net carbohydrate content per serving.
- Low-Sodium Meal Plan: Opt for low-sodium or no-salt-added seaweed salad. Rinse the salad thoroughly before consuming to further reduce sodium content. Pair it with dishes naturally low in sodium, such as grilled vegetables or lean protein.
Dietary Restrictions and Considerations
Several factors should be considered before incorporating seaweed salad into your diet.
- Iodine Sensitivity: Seaweed is a significant source of iodine. Individuals with iodine sensitivity or thyroid conditions should consume seaweed salad in moderation or consult their doctor before regular consumption.
- Heavy Metal Contamination: Seaweed can absorb heavy metals from the surrounding water. Choosing seaweed from reputable sources that undergo rigorous testing for heavy metal contamination is crucial to minimize risk. Look for certifications indicating quality control.
- Sodium Content: Many commercially prepared seaweed salads are high in sodium. Individuals on low-sodium diets should carefully check nutrition labels and choose low-sodium options or rinse the salad thoroughly before eating.
- Additives and Preservatives: Some seaweed salads contain added sugar, artificial flavors, or preservatives. Opt for minimally processed varieties with simple ingredients to maintain a healthier dietary choice.
Preparation and Serving Suggestions for Seaweed Salad
Seaweed salad, a refreshing and nutritious dish, is surprisingly easy to prepare at home. With readily available ingredients and a few simple techniques, you can create a delicious and customizable seaweed salad to enjoy as a side dish, a part of a larger meal, or even as a standalone appetizer. This section will guide you through the process, offering various options for preparation and serving.
Sourcing Ingredients and Basic Preparation Techniques, Seaweed salad nutrition facts
The foundation of any good seaweed salad lies in the quality of its ingredients. Begin by sourcing dried seaweed sheets, commonly available in Asian grocery stores or online. Look for varieties like wakame, dulse, or arame, each offering a slightly different flavor and texture. For added flavor and visual appeal, you can incorporate other vegetables such as shredded carrots, cucumbers, and bell peppers.
Sesame seeds are a common addition, offering a nutty flavor and pleasant crunch. Once you have your ingredients, rinse the dried seaweed thoroughly under cold water until it softens and expands. This usually takes around 5-10 minutes, depending on the type of seaweed. Then, finely chop or shred the seaweed to your desired consistency. Prepare the other vegetables by washing, peeling (if necessary), and cutting them into similarly sized pieces.
Dressing and Seasoning Options
The dressing is crucial in determining the final flavor profile of your seaweed salad. A simple sesame oil dressing, combined with rice vinegar, soy sauce, and a touch of sugar, is a classic choice. Many variations exist, reflecting different cultural influences. A Korean-inspired dressing might incorporate gochujang (Korean chili paste) for a spicy kick, while a Japanese-inspired version might use mirin (sweet rice wine) for a subtle sweetness.
For a lighter option, consider using a citrus-based vinaigrette with lemon or lime juice. Experiment with different combinations of sesame oil, rice vinegar, soy sauce, mirin, gochujang, ginger, garlic, and various spices to create your own unique dressing. Remember to adjust the seasoning to your taste preferences.
Incorporating Seaweed Salad into Various Dishes
Seaweed salad’s versatility makes it a welcome addition to a wide array of dishes.
- Sushi: Seaweed salad can be used as a filling inside sushi rolls, adding a refreshing and slightly salty element to the overall flavor profile.
- Soups: Adding seaweed salad to miso soup or other light broth-based soups provides a textural contrast and a boost of nutrients.
- Salads: Seaweed salad pairs well with other leafy greens and vegetables in a mixed salad, adding a unique dimension to the texture and taste.
- Side Dish: Served as a simple side dish, seaweed salad offers a light and healthy accompaniment to heavier main courses, balancing the meal.
Visual Appeal, Texture, and Appearance
A well-prepared seaweed salad is visually appealing, boasting a vibrant green color from the seaweed, complemented by the contrasting colors of other vegetables like orange carrots and red bell peppers. The texture is a delightful mix of soft, yielding seaweed and the crisp crunch of added vegetables and sesame seeds. The overall appearance is one of freshness and lightness, making it an attractive addition to any meal.
The seaweed itself has a delicate, almost translucent quality when hydrated, creating an appealing contrast with the firmer textures of other ingredients.
Clarifying Questions: Seaweed Salad Nutrition Facts
Is seaweed salad a good source of protein?
While not a primary protein source, seaweed salad does provide a modest amount of protein, contributing to overall daily intake.
Can I eat seaweed salad every day?
Moderation is key. Daily consumption is generally safe for most individuals, but those with iodine sensitivity should consult a doctor before regular intake.
Does seaweed salad contain any harmful substances?
Some seaweeds can accumulate heavy metals. Choosing reputable brands and sources helps minimize this risk.
How long can I store seaweed salad?
Refrigerate leftover seaweed salad promptly and consume within 3-5 days for optimal freshness and quality.
Is seaweed salad suitable for people with diabetes?
Seaweed salad’s low glycemic index and fiber content can be beneficial for blood sugar management, but individual responses may vary. Consult a doctor or registered dietitian for personalized advice.
